What is the role of Merchant Banker?
Merchant Bankers or the Book running lead Managers have become a crucial part of the financial and credit system as they play an important role in assisting the Small and Mid- size companies (SMEs) to raise funds through IPOs, debt Issue or private equity. They also provide advisory services.
SMEs usually have requirement of funds to fuel their business growth through expansion and thereby Merchant Banking has become a valuable financial service for SMEs to raise capital through Primary Issue (SME IPO). Merchant bankers also provide advice and assistance in areas of financial management and corporate restructuring.
What role does IPO Advisors play in successful IPO?
IPO Advisors play an important role in successful launch of an IPO. Their advisory role from IPO readiness, selecting the best merchant banker in India for SME IPO, various due diligence activities and IPO valuation guides the company throughout the IPO Issue and listing process. IPO platform in India provides information on upcoming IPOs on NSE Emerge and BSE SME and list of merchant bankers and anchor investors. Role of IPO advisor is important in the success of the listings.
Functions of a Merchant Banker
- Management of public Issues
- The role and responsibility of merchant banker is broader in SME IPO as their role starts from the IPO process up to the post IPO phase.
- A merchant banker is responsible to carry out the entire IPO process for SME which includes Due Diligence, preparing DRHP, RHP and documentation.
- A Merchant Banker arrives at a fair valuation of the business for the purposes of IPO. Valuation is based on analysis of financial data, assessing the key market trends, peer analysis and sector information.
- 100% of the Issue is underwritten and further it is compulsory for a merchant banker to underwrite 15% of the Issue size in its own books.
- Merchant banker has to ensure Market making for a period of 3 years from the date of listing. Market makers are appointed for this purpose.
- As per the provisions of chapter XB of the ICDR, merchant banker can enter into arrangements with nominated investors (PE funds & QIBs as defined therein) for the purposes of market making and underwriting. The merchant bankers are required to disclose this arrangement with Nominated investors to the exchange in the Final Offer document.
- Loan Syndication- Merchant bankers act as an intermediary between the borrowers and the lenders. They are involved in all the steps of loan processing and approval.
- Private Equity and Venture capital- Some of the Merchant bankers also help the start ups and mid -size companies to raise funds through private equity or venture capital.
- Corporate Finance Advisory- Some merchant bankers offer advice on financial matters like restructuring, capital raising strategies and regulatory compliances thus assist a company to use its financial resources effectively.
- Asset management- Some Merchant Bankers also manage investment portfolios on behalf of individual and institutional clients like mutual funds, hedge funds and others.
What are the different categories of Merchant Banker?
Merchant Bankers are broadly classified in 2 categories as per the amended Merchant Bankers Regulation, 1992 on basis of net worth and activities.
Category I Merchant Bankers: This is the most comprehensive category, where firms are involved in the full process of Issue management. They also act as underwriters and portfolio managers. Category I is the top tier merchant bankers in India certified by SEBI. Net worth of this category of merchant bankers shall not be less than Rs 50 crores.
Category II Merchant Bankers: Firms in this category provide advisory, consulting, and management services in IPO. Net worth shall not be less than Rs. 10 crores and allowed to undertake all permitted activities except managing equity issues on the Main Board.
Here are some key points from amendments in Merchant Banker Regulation Act:
- MBs shall maintain a liquid net worth of at least 25% of the minimum net worth requirement, at all times.
- The underwriting limit for MBs has been prescribed as 20 times of liquid net worth.
- A merchant banker shall not lead manage any public issue, if its directors, other key managerial personnel, compliance officer, employees or relative(s) of the said persons, individually or in aggregate hold more than 0.1% of paid up share capital or shares whose nominal value is Rs. 10,00,000, whichever is lower, in the Issuer company. Such MB may be appointed, if it is involved only in the marketing of the issue, subject to appropriate disclosures.
What are the IPO cost charged by the Merchant banker in India?
Merchant Banking cost or fee forms the major portion of IPO cost for the Issuer. The Book running lead managers role ranges from DRHP preparation, filing, marketing, valuations and assisting the company post listing also. They coordinate with various intermediaries for successful completion of IPO. Detailed and tentative cost can be understood from IPO cost blog.
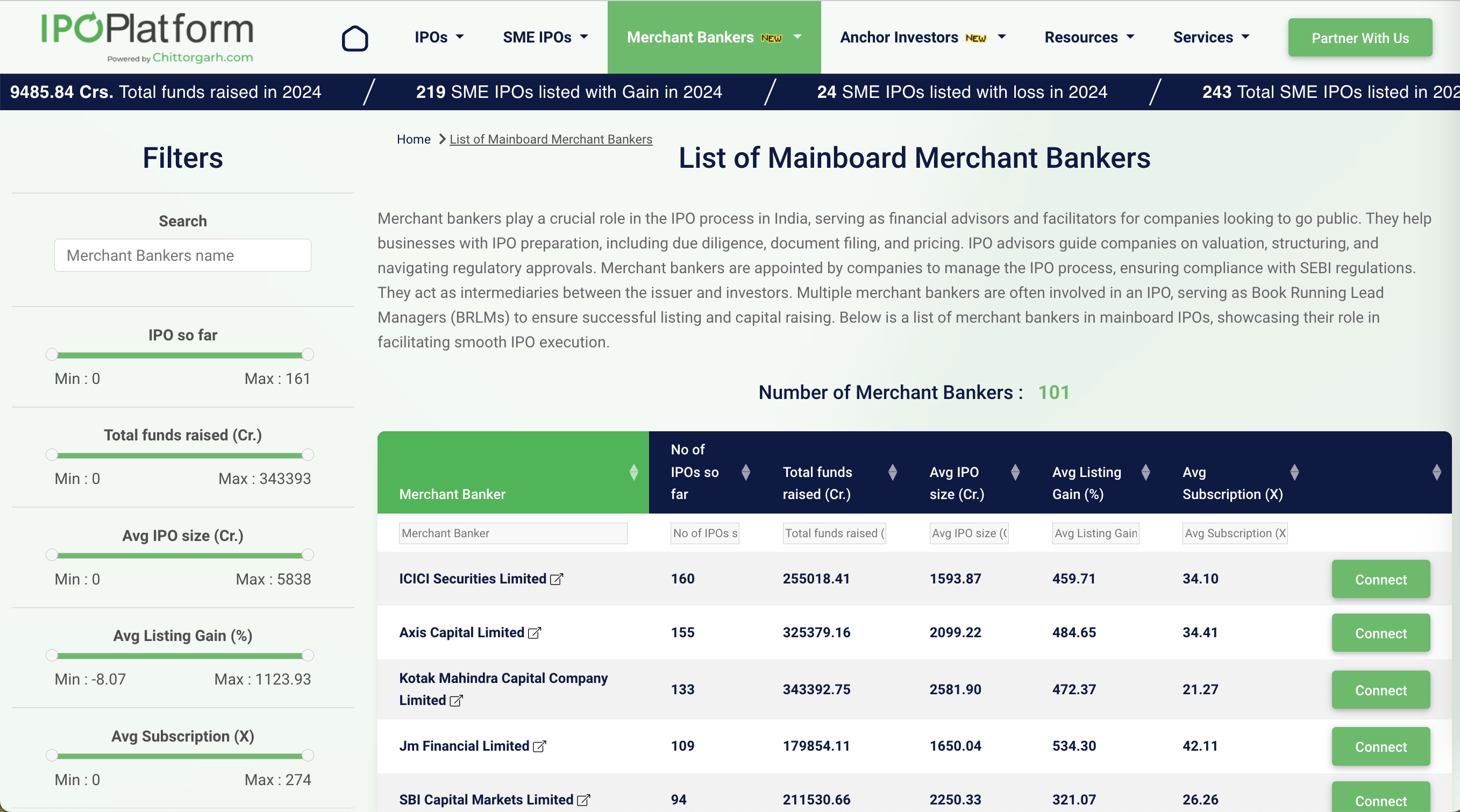
List of Top Merchant bankers in Mainboard IPO
See the full list of Merchant Banker here https://www.ipoplatform.com/merchant-bankers-mainboard-list
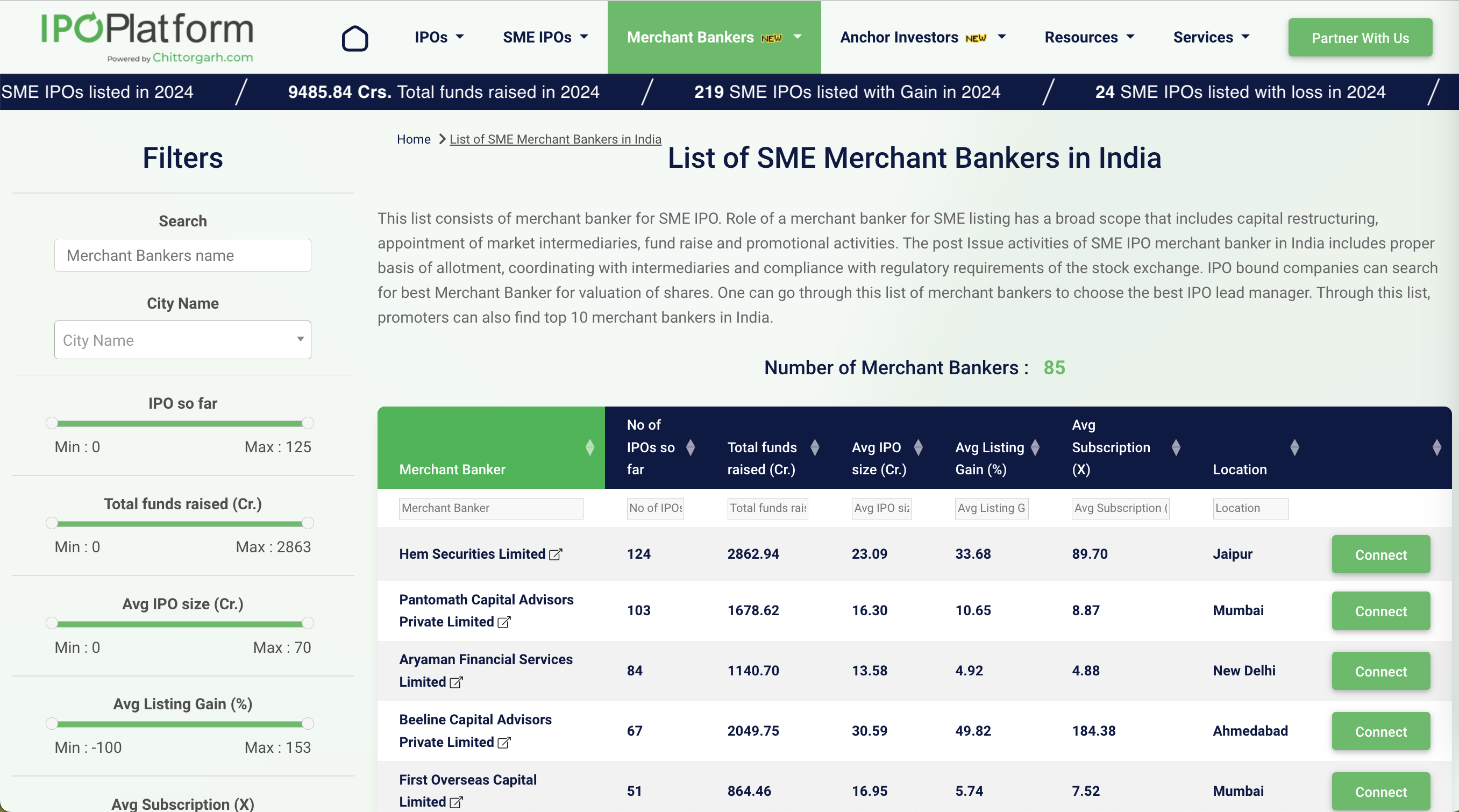
List of Top Merchant bankers in SME IPO
See the full list of Merchant Banker here https://www.ipoplatform.com/merchant-bankers-list
How Merchant Bankers Help in the Due Diligence Process?
A company has to comply with the IPO eligibility criteria for the purposes of IPO and listing on NSE Emerge or BSE SME or NSE and BSE for Mainboard IPO.
Merchant bankers play a very important role in the due diligence process, which is the detailed investigation conducted before a financial transaction, like an IPO (Initial Public Offering) or a merger, takes place. It’s the prime responsibility of merchant banker to ensure that all aspects of the deal are thoroughly checked to bring transparency and accuracy in the ecosystem.
- Financial Assessment: They review a company's financial health by examining balance sheets, profit & loss statements, and cash flow. This ensures that investors have a clear picture of the company’s financial position.
- Legal Review: Merchant bankers also look into any legal issues that could impact the deal, such as ongoing litigations or compliance with regulations. They help identify any potential legal risks.
- Operational Inspection: They assess the company’s operations, including management, systems, and processes, to make sure everything is running smoothly and efficiently.
- Risk Assessment: Book Running Lead Managers of BRLMs assess risks and potential challenges surrounding a particular Issue on a case to case basis.
Due Diligence process helps in reducing risks for investors, increase trust, and ensure that the transaction is fair and well-informed.
What are the Roles and Responsibilities of Merchant Banker in Mainboard IPO and SME IPO?
The Issuer shall appoint merchant Bankers which are registered with the SEBI. Merchant bankers have to manage the rights, obligations and responsibilities related to Issue, disclosures, underwriting obligations etc.
These are the following roles and responsibilities of the Merchant bankers;
1. Due Diligence:
Merchant Bankers helps the Issuer company in the whole process of the Due diligence. Due Diligence is very important process for company before going public. Due Diligence is a process of gathering various information of the company and get them reviewed and documented. This process includes:
- Gathering all the organizational data;
- Collate all audit reports, Board reports, all details related to Directors and Employees and KMP of the Issuing Company;
- Gathers all the data related to Finance, Legal and Compliances requirements;
- Information regarding Market growth and verifying company’s assets.
2. IPO Valuation:
Merchant Bankers review the financial data of the company and demand of IPO in the market for that industry or sector. IPO valuation i.e. the P/E metrics is arrived at after analyzing the peers and the sector. Various other factors like future projections also affect the valuations. (IPO Valuation blog link)
3. IPO Structure:
The merchant banker and the Issuer jointly prepare IPO Structure and other related information and execute the structure of the SME IPO. Together, they finalize the details of the offering, which include:
- Type of Securities: Deciding on the category of securities to be listed.
- Quantity of Shares: Determining the total number of shares to be offered. Any bonus Issue requirement is also considered.
- Share Payment Terms: Specifying whether the shares are fully paid-up or partly paid-up.
- Face Value: Setting the nominal or par value of the shares.
- Lot Size and Minimum Order: Establishing the minimum number of shares per lot and the smallest order size for investors.
- Pricing Strategy: Finalizing the method and price range for the offer.
- Investor Categories (link): Allocating proportions for anchor investors, retail investors, qualified institutional buyers (QIBs), and non-institutional investors (NIIs).
- Offer Timeline: Defining the booking period for the IPO.
- Special Reservations: Deciding on employee reservations, employee discounts, and the allocation for the market maker.
4. Drafting of the Contracts:
Merchant bankers help companies to draft the contracts with various Intermediaries involved in the Issue and these includes following drafts;
-
Tripartite Agreement: Between NSDL, CDSL, and the Registrar to the Issue.
- Underwriting Agreement: Defining the underwriting commitments.
- Market Making Agreement: Outlining the role of the market maker.
- Bankers to the Issue Agreement: Agreement with banks handling IPO funds.
- Registrar Agreement: Agreement with the Registrar to the Issue.
- Board/Shareholder Resolutions: Approvals from the company's board or shareholders.
- Certificates and Declarations: Relevant representations and certifications.
- Public Notices and Announcements: Drafts for investor communication.
- Regulatory Forms: Applications for submission to the stock exchange, RoC, and other regulatory bodies.
5. Preparing and Drafting DRHP (Draft Red Herring Prospectus)
Merchant Banker is responsible for preparation and filing of DRHP (link) with the respective stock exchange. DRHP is a very important document that includes key information relating to the Issue, Promoters, financial statements, company information and other details. In Mainboard IPO the DRHP is review by SEBI while in SME IPO the DRHP is reviewed by Stock Exchanges. (link to difference between SME IPO and mainboard IPO)
6. Underwriting:
It is mandatory for all SME IPOs to be fully (100%) underwritten. In a SME IPO Merchant Bankers must underwrite at least 15% of the IPO shares. The remaining 85% can be managed by a third-party fund manager. However, there is no requirement of underwriting in a Mainboard IPO.
7. Marketing and advertisement:
Merchant bankers play a very major role in marketing of the Issue and creating demand of IPO in the market. The main object of advertising the IPO is to attract investors and build confidence amongst the investors for IPO company.
What are the Post Issue Activities of the Merchant Banker as a Book Running Lead Manager?
- Listing related- They continue to be responsible until all applicants have received their securities credited to their Demat accounts, or refunds of their application money and the issuer's listing agreement is finalized with the stock exchange. They must monitor redressal of investor grievances that arise from the Issue.
- Intermediaries Related- They work with the registrars and other intermediaries to ensure smooth processing after the Issue closes, including tracking applications, allotments, crediting securities to demat accounts, and handling refunds. If any act of omission or contraventions are done by the intermediaries, and same noticed by the lead manager(s) than they must have to report it to the Board.
- Underwriting related- In case if underwriters fail to meet their commitments, the lead manager(s) must issue a notice within 10 days after the issue closes. In the case of an undersubscribed issue, the lead manager(s) shall furnish information in respect of underwriters who have failed to fulfill their obligations to the Board in form specified in Schedule XVIII.
- Utilisation of Issue Proceeds- Merchant Bankers in India are responsible to furnish a report on utilization of Issue proceeds on half yearly basis.
How to choose best merchant banker?
Choosing the best merchant banker is very important step in the process of going public. A company shall make a careful evaluation to ensure they align with company’s profile and have experience working with similar businesses and sector. Choosing the Merchant Banker plays a major role in the success of IPO.
Here are some key factors to consider;
- Industry Expertise: While selecting the merchant banker, a company must ensure that the merchant banker have the strong understanding of that industry. This ensures that they can effectively highlight business's strengths to potential investors. Understanding industry insights and peers can be helpful for IPO valuations.
- Research Capabilities: Looking for a merchant banker who is committed to provide quality research on the market trends and future growth potential of that particular sector or industry, which helps in accurately presenting your company’s value and growth potential.
- Investor Relations: Issuer company will want to choose a merchant banker who has an established relationship with a wide network of investors to ensure better outreach and participation of investor in the Issue.
- Proven Track Record: Company while selecting a Merchant banker must check their past performance, including successful IPOs or fund-raising efforts for companies similar to them. It gives them insights of work done by merchant banker in past and how it is going. A strong track record reflects their expertise and reliability.
- Market Making Arrangements: While choosing a Merchant banker company should ensure that the banker has the capability to make arrangements for market making, which is very important part for maintaining liquidity in company’s stock post-IPO. Market making is compulsory in a SME IPO for listing on NSE Emerge or BSE SME platform.
By assessing these factors, Company can select a merchant banker who fits best for company’s needs and can effectively manage the public offering.
Conclusion
Merchant bankers are pivotal to the success of IPOs and financial transactions. They provide essential services ranging from advisory roles to underwriting, valuation, and marketing, ensuring that both companies and investors are well-prepared for the public offering. Choosing the right merchant banker is a critical decision for any company looking to go public, and careful evaluation of the banker’s experience, expertise, and track record can significantly impact the success of the IPO process.
For further insights and information, you can explore our full list of top merchant bankers in both Mainboard IPOs and SME IPOs through the provided links.





0 Comments